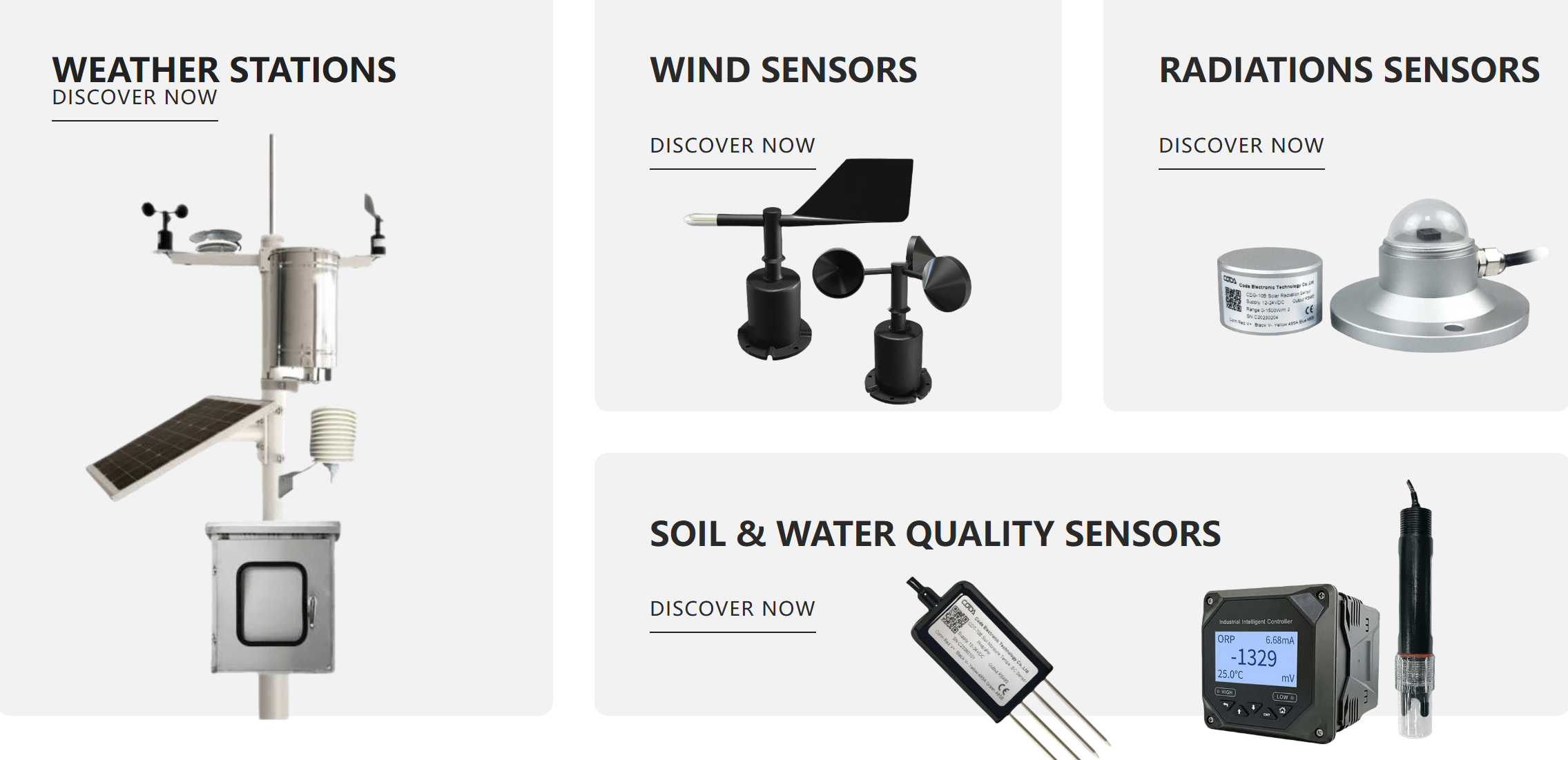
Meteorological Technology Breakthrough: How Sensors Are Transforming Weather Monitoring
Outline
-
Introduction
-
Importance of weather monitoring
-
Limitations of traditional meods
-
Rise of meteorological sensors
-
Theme Analysis: How Meteorological Sensors Drive Change in Weather Monitoring
-
Core technologies of meteorological sensors
-
Wide range of application fields
-
Data-driven precision forecasting
-
Guide: How to Optimize Weather Monitoring with Meteorological Sensors
-
Types and selection of meteorological sensors
-
Equipment installation and layout strategies
-
Tips for data collection and processing
-
Tutorial: Practical Steps to Build a Modern Meteorological Sensor Network
-
Step 1: Identify monitoring goals and requirements
-
Step 2: Select suitable sensor equipment
-
Step 3: Deploy and calibrate the sensor network
-
Step 4: Build data integration and analysis platforms
-
Case Studies: Applications of Meteorological Sensors in Real-World Scenarios
-
Precision meteorological services in agriculture
-
Urban environmental monitoring and warning systems
-
Data support during extreme weather events
-
Conclusion and Outlook
-
Current status and future potential of meteorological sensors
-
Relationship between meteorological technology and sustainable development
-
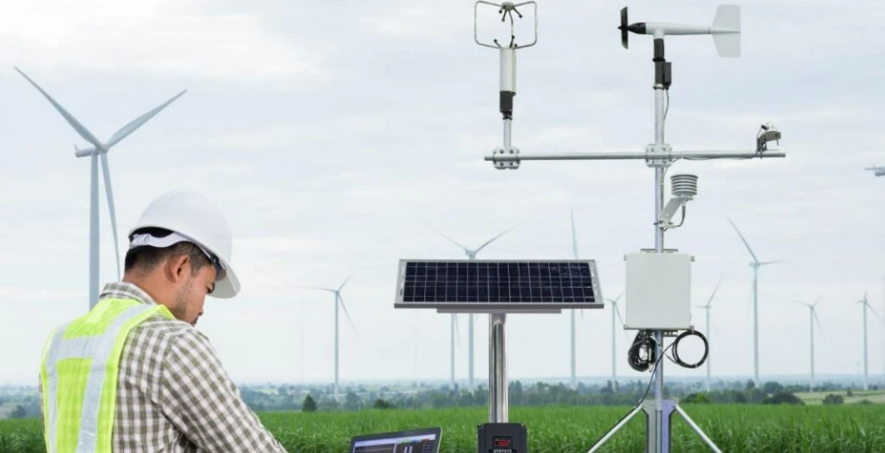

Main Article
Introduction
Weather plays a crucial role in daily life and economic activities, making accurate weather monitoring essential for sectors like agriculture, transportation, and energy. However, traditional meods often fall short due to sparse equipment, limited coverage, and insufficient real-time data. In this context, meteorological sensor technology has emerged as a game-changer, driving the evolution of weather monitoring into an era of intelligence and data-driven insights.
Theme Analysis: How Meteorological Sensors Drive Change in Weather Monitoring
-
Core Technologies of Meteorological Sensors
Meteorological sensors utilize physical, chemical, and electronic principles to measure parameters like temperature, humidity, atmospheric pressure, wind speed, and precipitation. These sensors provide greater accuracy and sensitivity than traditional equipment, particularly in localized or specific environments. -
Wide Range of Application Fields
Meteorological sensors are widely used in agriculture, climate research, traffic safety, and environmental protection. For example, in precision agriculture, sensors deliver real-time weather data to optimize irrigation and fertilization strategies. In urban environments, they monitor air quality and offer actionable insights for municipal authorities. -
Data-Driven Precision Forecasting
Networks of meteorological sensors generate vast amounts of data, enriching weather forecasting models with detailed input. Combined with machine learning and big data analytics, scientists can issue early warnings for extreme weather events, mitigating potential losses.
Guide: How to Optimize Weather Monitoring with Meteorological Sensors
-
Types and Selection of Meteorological Sensors
-
Temperature Sensors: Measure air or surface temperatures.
-
Humidity Sensors: Monitor changes in air humidity.
-
Pressure Sensors: Provide atmospheric pressure data to support forecasting models.
-
Wind Speed and Direction Sensors: Track wind changes for aviation and maritime activities.
-
Rain Gauges: Record precipitation intensity and volume, crucial for flood prevention and water resource management.
-
Equipment Installation and Layout Strategies
-
Ensure sensor installation sites are free from obstructions to avoid distorted data.
-
Strategically place sensors based on the terrain and monitoring objectives to cover critical areas.
-
Regularly inspect and maintain equipment for stable, long-term operation.
-
Tips for Data Collection and Processing
-
Use automated systems to reduce manual intervention.
-
Upload data to cloud platforms for remote management and real-time analysis.
-
Employ visualization tools to present trends clearly, aiding interpretation and decision-making.
Tutorial: Practical Steps to Build a Modern Meteorological Sensor Network
-
Identify Monitoring Goals and Requirements
Define the parameters to be monitored, such as temperature, humidity, or extreme events like storms. Tailor your goals to the target area’s characteristics (e.g., agriculture, urban environments). -
Select Suitable Sensor Equipment
Choose devices based on measurement range, accuracy, durability, and cost. For long-term use, prioritize energy-efficient and stable equipment. -
Deploy and Calibrate the Sensor Network
-
Install multiple sensors across the target area to ensure comprehensive data coverage.
-
Calibrate sensors initially to validate accuracy.
-
Configure network connectivity for real-time synchronization with data platforms.
-
Build Data Integration and Analysis Platforms
-
Develop a platform to aggregate and process data from various sensors.
-
Use analytics tools to extract key insights, such as trends or anomalies.
-
Integrate with third-party applications to automate alerts and generate reports.
Case Studies: Applications of Meteorological Sensors in Real-World Scenarios
-
Precision Meteorological Services in Agriculture
A farm implemented meteorological sensors to monitor soil moisture and weather changes. By leveraging the data, they optimized irrigation systems, reducing water usage by 30% and increasing crop yield. -
Urban Environmental Monitoring and Warning Systems
A smart city deployed hundreds of sensors to monitor air pollution, rainfall intensity, and road slipperiness. The system provided real-time alerts to citizens, significantly reducing traffic accidents. -
Data Support During Extreme Weather Events
During a typhoon, a sensor network provided real-time wind speed and atmospheric pressure data, enabling local authorities to make accurate decisions and evacuate at-risk residents successfully.
Conclusion and Outlook
Meteorological sensors are transforming traditional weather monitoring, enhancing prediction accuracy and providing economic and societal benefits across various industries. As sensor technologies advance and integrate further with artificial intelligence, weather monitoring will become increasingly intelligent and automated, supporting sustainable development worldwide.
By effectively utilizing meteorological sensors and managing weather data scientifically, we can better address climate change and extreme weather challenges, building a safer and more efficient future.